What Is a Milling Machine? Your Essential Guide to Precision Manufacturing
Milling machines are the precision shapers of modern industry. Using high-speed rotating cutters, they carve materials into components ranging from simple flats to complex 3D contours. As core equipment in aerospace, automotive, and mold-making sectors, these machines deliver unmatched accuracy, versatility, and efficiency.
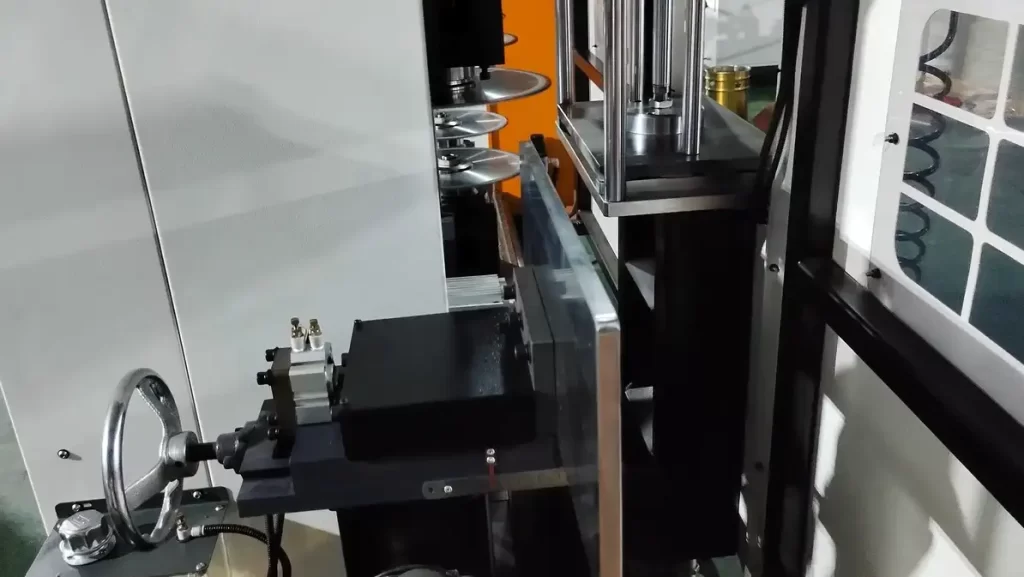

Milling Machine Construction and Machining Principles
Core Components
Think of a milling machine as a coordinated precision system:
- Machine Bed: This cast-iron foundation absorbs vibrations and ensures stability.
- Spindle: The rotating “heart” driving cutters at 500-20,000 RPM.
- Worktable: Moves along X/Y/Z axes (±0.01mm accuracy) to position workpieces.
- Feed System: Uses servo motors for micron-level movement control.
- Cooling System: Sprays fluid to reduce heat and clear chips.
- ATC (Automatic Tool Changer): Swaps tools in seconds on advanced models.
How Milling Works
Essentially, rotating multi-edge cutters remove material while the workpiece moves along programmed paths. Two primary methods exist:
- Climb Milling: Tool rotation matches feed direction. Result: Smoother finishes, ideal for final passes.
- Conventional Milling: Tool opposes feed direction. Result: Higher cutting force, better for roughing.
Optimize these parameters for your material:
| Parameter | Impact | Example Settings |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Speed | Surface finish, tool wear | Aluminum: 150-200 m/min |
| Feed Rate | Machining time, chip thickness | Finishing: 0.01 mm/rev |
| Depth of Cut | Material removal rate | Steel: ≤1 mm/pass |
Warning: Incorrect settings cause rough surfaces or tool damage.
Types and Applications of Milling Machines
Machine Types Compared
- Vertical Mills: Compact spindle-perpendicular-to-table design. Best for: Electronics housings.
- Horizontal Mills: Spindle parallel to table. Best for: Heavy bases/gearboxes.
- CNC Mills: Computer-controlled (±0.005mm precision). Best for: Complex aircraft parts.
- Universal Mills: Adjustable spindles/tables. Best for: Curved surfaces.
- Machining Centers: All-in-one milling/drilling. Best for: High-volume production.
Top 5 Cutting Tools
- End Mills: General-purpose slotting/finishing
- Slot Drills: Deep grooves/mold cores
- Ball Nose Cutters: 3D contours (e.g., turbine blades)
- Face Mills: Rapid surface leveling
- T-Slot Cutters: Workholding fixtures
Key Industries Served
- Aerospace: Titanium engine components
- Automotive: Engine blocks (50,000+ units/year)
- Medical: Stainless steel joint implants
- Mold & Die: Injection molding cavities
- Energy: Turbine blade profiling
Selection, Operation & Maintenance Guide
Choosing Your Machine
Follow this decision framework:
- Part Size: Small? Pick vertical mills. Large? Choose horizontal.
- Precision Needs: ±0.1mm? Manual OK. ±0.01mm? Require CNC.
- Budget Range:
- Manual: ¥50,000-150,000
- CNC: ¥200,000+ Tip: Factor in tooling/fixture costs (15-20% extra).
Safe Operation Protocol
- Always wear ANSI-rated goggles and gloves.
- Verify workpiece clamping force exceeds cutting forces.
- Program CNC units using CAM software (e.g., Fusion 360).
- Immediately stop if vibration/chatter occurs.
Pro Maintenance Schedule
| Frequency | Task | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Daily | Clean chips/lubricate guides | Prevents accuracy drift |
| Monthly | Replace coolant/filters | Avoids corrosion |
| Quarterly | Calibrate spindle/axes | Maintains ±0.01mm tolerance |
Pro Tip: Modern CNCs self-diagnose 80% of faults via IoT sensors.
Conclusion & FAQs
Ultimately, milling machines enable mass production of precision parts unreachable by other methods. Future trends include AI-driven optimization and eco-coolants.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Milling machine vs. lathe?
A: Mills rotate tools on stationary workpieces (flats/contours). Conversely, lathes rotate workpieces against tools (cylinders/shafts).
Q: Is CNC operation difficult?
A: Basic functions take 1-2 weeks to learn. However, mastering G-code/CAM requires 3-6 months.
Q: How to select cutters?
A: Follow this guide:
- Hard materials (steel): Carbide-coated tools
- Soft materials (aluminum): High-speed steel
- Curved surfaces: Ball nose end mills
Q: Maintenance complexity?
A: Surprisingly simple: Daily cleaning (10 mins) and quarterly calibrations prevent 90% of issues.