The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Best CNC Machining Centers in 2025
1. Why Choosing the Right CNC Machining Center Matters
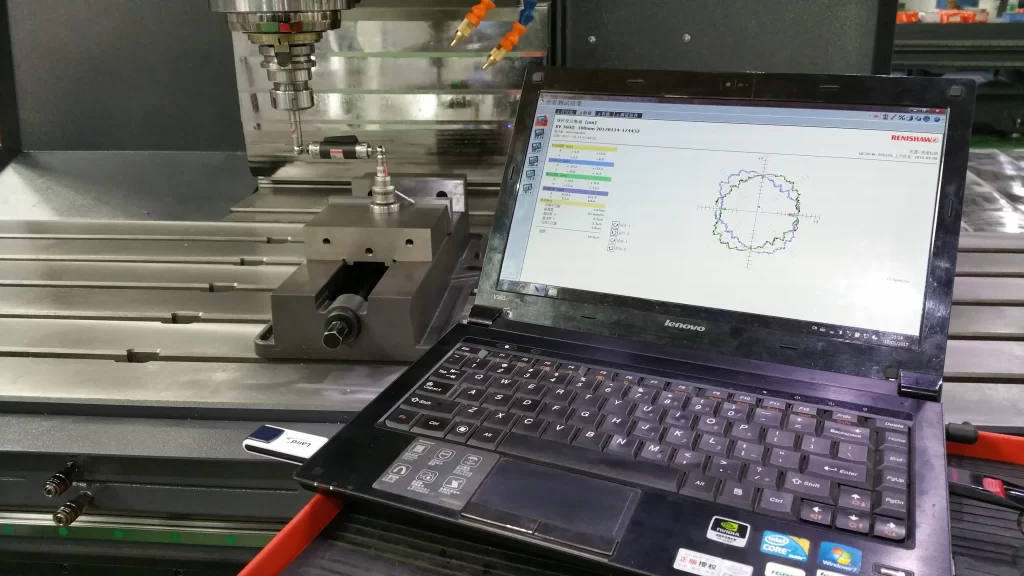
CNC machining centers (Computer Numerical Control equipment) are the backbone of modern manufacturing, powering industries like automotive, aerospace, renewable energy, rail transport, and 5G electronics with precision and efficiency. Picking the right machine isn’t just about buying equipment—it directly impacts productivity, cost management, and product quality. A high-precision CNC machine can boost your output of quality parts by over 10%, while a poor fit could double your rework rate. The key is aligning the machine with your industry’s needs: automotive demands speed, aerospace requires micron-level accuracy.
The goal is to strike a balance between performance and your specific requirements. For instance, electric vehicle production calls for lightweight material processing, while 5G manufacturing prioritizes ultra-high precision and stability. When selecting a machine, evaluate spindle speed (which drives cutting efficiency), control systems (like Fanuc or Siemens, affecting operational flexibility), and automation features to avoid future headaches. A well-chosen machine not only ramps up production but also cuts maintenance costs, giving your business a competitive edge. This guide offers a clear roadmap, covering machine types, industry applications, and selection criteria to help businesses—small or large—make informed decisions.
2. Key Types of CNC Machining Centers

CNC machining centers come in various types, each with unique strengths. Understanding their technical specs and ideal use cases is critical before making a purchase.
- Vertical Machining Center (VMC) Compact and space-efficient, VMCs are ideal for flat or shallow-cavity parts, like engine covers or chassis components in the automotive industry. With tools moving along a vertical axis, they’re user-friendly and cost-effective, priced between $70,000 and $280,000, making them a go-to for small and medium-sized businesses.
- Horizontal Machining Center (HMC) Designed for multi-sided machining, HMCs have a horizontally oriented spindle, allowing easy workpiece rotation and fewer re-clamping steps, boosting efficiency. They’re perfect for aerospace parts like turbine blades or complex structural components and excel in high-volume production. Prices range from $140,000 to $560,000.
- Five-Axis Machining Center A powerhouse for precision, five-axis machines move along three linear and two rotational axes, ideal for complex surfaces like 5G antenna components or medical implants. They cut processing time and deliver superior accuracy but come with a price tag of $280,000 to $1.1 million, suited for high-precision applications.
- Multi-Tasking Machine (MTM) The all-in-one solution, MTMs combine turning, milling, and other processes in a single setup, perfect for complex parts like rail transport axles or gears. Priced between $420,000 and $1.4 million, they’re ideal for intricate, high-end applications.
When choosing, align the machine type with your part complexity, production volume, and budget to find the best fit.
3. Core Evaluation Criteria for CNC Machining Centers

Selecting a CNC machining center requires evaluating key technical parameters to ensure it meets your production needs.
- Machining Accuracy Accuracy, measured in microns (tolerance range), determines part quality. Aerospace and 5G industries demand tolerances as tight as ±0.005mm, while automotive parts typically require ±0.01mm. Check the machine’s positioning and repeatability specs in its technical documentation.
- Spindle Speed and Power Spindle speed (in RPM, revolutions per minute) and power dictate material compatibility. High-speed spindles (10,000–20,000 RPM) handle aluminum or composites, while high-power spindles (20–40kW) tackle steel or titanium. Electric vehicle battery casings need high RPM for surface finish, while aerospace parts require power for tough materials.
- Control System The control system is the machine’s brain. Fanuc systems are known for reliability and ease of use, ideal for quick adoption. Siemens systems offer advanced programming for complex tasks like multi-axis machining. Choose based on your team’s expertise and task complexity.
- Worktable Size and Load Capacity Worktable size and load capacity determine the size of parts you can machine. 5G components need smaller tables (around 20×20 inches), while rail transport requires large tables capable of handling tons. Verify size and load specs in the machine’s manual.
- Automation Features Features like Automatic Tool Changers (ATC) and robust clamping systems boost efficiency. A fast ATC (under 5 seconds) is ideal for high-volume production. Evaluate tool change speed and clamping system compatibility to match your production pace.
4. Industry Applications and Machine Matching

Different industries have unique needs, and matching the right CNC machine to your goals is critical for efficiency and quality.
- Automotive Industry Focused on high-speed, high-volume production for parts like engine blocks and brake discs. Vertical machining centers with 10,000–15,000 RPM spindles are recommended for fast aluminum or steel processing. Deli CNC’s VMC series offers great value for small to medium batch production.
- Electric Vehicles Battery casings and motor components demand high surface finish and complex geometries. Five-axis machining centers with high RPM and reliable cooling systems are ideal for lightweight aluminum alloys. Deli CNC’s five-axis models excel in these precision-driven tasks.
- Aerospace Requires ultra-tight tolerances (±0.005mm) for parts like turbine blades and structural components. Five-axis machines with Siemens SINUMERIK controls and 20–40kW spindles handle complex geometries and tough materials like titanium. Deli CNC’s aerospace-specific five-axis machines are a strong choice.
- Rail Transport Large, heavy parts like axles and wheelsets need high-load horizontal machining centers with worktables supporting several tons. Multi-sided machining reduces re-clamping, saving time. Machines with ATCs are recommended for efficiency.
- 5G and Electronics Micro-components like antenna parts and circuit board housings require high-precision machines. High-speed five-axis or compact CNCs with 20,000+ RPM spindles and micro-tools (under 1mm diameter) are ideal. Deli CNC’s compact precision models suit these low-tolerance needs.
| Industry | Core Needs | Recommended Machine | Key Parameters | Typical Parts |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | High efficiency, volume | Vertical Machining | 10,000–15,000 RPM spindle | Engine blocks, brake discs |
| Electric Vehicles | Lightweight, high finish | Five-Axis Machining | High RPM, stable cooling | Battery casings, motor parts |
| Aerospace | High precision, complex | Five-Axis Machining | ±0.005mm tolerance, 20–40kW | Turbine blades, structures |
| Rail Transport | Large parts, high load | Horizontal Machining | Large worktable, high load | Axles, wheelsets |
| 5G & Electronics | Micro parts, high precision | High-Speed Five-Axis/Compact CNC | 20,000+ RPM, micro-tools | Antennas, circuit housings |
5. Budget and Cost-Effectiveness Analysis
Initial Investment Costs
CNC machining centers vary widely in price. Vertical machining centers range from $70,000 to $280,000, ideal for small businesses. Horizontal machines cost $140,000 to $560,000 for high-volume needs. Five-axis machines run $280,000 to $1.1 million for precision tasks, while multi-tasking machines are $420,000 to $1.4 million for complex processes. Match your production goals and precision needs to avoid overspending.
Long-Term Operating Costs
Maintenance, including routine servicing and part replacements (e.g., spindle bearings, tools), can cost $4,000 to $40,000 annually. Energy consumption varies: vertical machines use 10–20kWh per hour, while multi-tasking machines may hit 50kWh. Component costs depend on the supplier—Fanuc parts are pricier than domestic alternatives. Review supplier maintenance plans and energy data to manage costs.
Balancing Performance and Budget
Mid-range machines like Deli CNC’s VMC series offer strong value for automotive and general manufacturing, ideal for budget-conscious factories. High-end five-axis or multi-tasking machines deliver superior performance but come with higher maintenance and operation costs, suited for well-funded or precision-critical operations. Assess production volume, material types, and tolerance needs to calculate ROI.
New vs. Used Equipment
Used machines can cost a third of new ones but risk wear or outdated tech, potentially increasing maintenance costs. New machines offer cutting-edge technology, warranties, and reliable support, ideal for long-term stability and advanced processes. For used machines, check usage history, spindle condition, and maintenance records.
6. Supplier Selection and Brand Evaluation
A supplier’s expertise shapes your machine’s performance and experience. Strong R&D delivers advanced control systems (CNC Control System), like IoT-enabled features for smarter production. Reliable after-sales support, with 24-hour response times and fast spare parts delivery, is critical. Evaluate suppliers through:
- Trade Shows: Events like IMTS or CIMT let you test machines and discuss specs with engineers.
- Case Studies: Review supplier success stories, like automotive engine block machining, to gauge capability.
- Customer Reviews: Check industry forums and third-party platforms for insights on machine reliability and service quality.
7. Technology Trends and Future-Proofing
Smart Manufacturing and IoT
AI and IoT (Internet of Things) integration transforms CNC machines, enabling self-optimization through real-time data analysis, like adjusting cutting parameters or detecting tool wear. These features suit automotive and 5G production. Prioritize machines with AI and IoT-compatible control systems.
Green Manufacturing
Energy-efficient motors and smart power management cut consumption (e.g., reducing vertical machine usage from 20kWh to 15kWh per hour). Eco-friendly materials and waste recycling systems align with electric vehicle and aerospace demands. Check energy specs and environmental certifications.
Modular Design
Modular designs allow upgrades like spindle enhancements or automated fixtures, ideal for rail transport’s evolving needs. Verify machine expandability and compatibility to ensure long-term value.
8. Implementation and Optimization Strategies
Machine Installation and Setup
Proper installation ensures reliable performance. Confirm the factory floor is level and meets load requirements. Follow the manufacturer’s manual for foundation anchoring and power connections. During setup, calibrate spindle accuracy and tool changer movements to micron-level precision. Verify the cooling system to prevent overheating. Use professional technicians to avoid setup errors.
Operator Training
Skilled operators maximize efficiency and quality. Train new hires on programming, workpiece fixturing, and tool selection. For complex tasks, use simulation software to master G-code (CNC programming language) and workflows. Regular advanced training on high-speed cutting or multi-axis techniques keeps your team sharp.
Regular Maintenance Plan
Extend machine life with consistent maintenance:
- Daily: Check lubrication systems for smooth operation and minimal wear.
- Weekly: Clear chips and coolant residue to maintain accuracy.
- Quarterly: Calibrate spindles and guide rails for stability.
- Annually: Inspect electrical and hydraulic systems to prevent issues.
Data-Driven Optimization
Modern CNC machines collect data on cutting speed, spindle load, and tool wear, enabling process improvements. Optimization steps:
- Gather temperature, vibration, and power data.
- Use analytics software to identify bottlenecks and adjust parameters.
- Update machining databases regularly to align with market demands. Data-driven approaches boost efficiency and reduce energy and material waste.