Metal CNC Machines: Techniques, Applications, And Selection Tips
MMetal CNC Machines harness Computer Numerical Control (CNC) technology to craft precision components, transforming industries like aerospace, automotive, medical, and electronics. These CNC machines deliver micron-level tolerances, automate workflows, and tackle complex geometries. For example, aerospace turbine blades achieve tolerances of ±0.005 mm, automotive CNC lathes cut material waste by 15%, and electronics enclosures maintain precision machining accuracy of ±0.01 mm. Curious about how Metal CNC Machines shape intricate designs? Dive in to explore their technology, applications, and tips for selecting the right CNC machines!
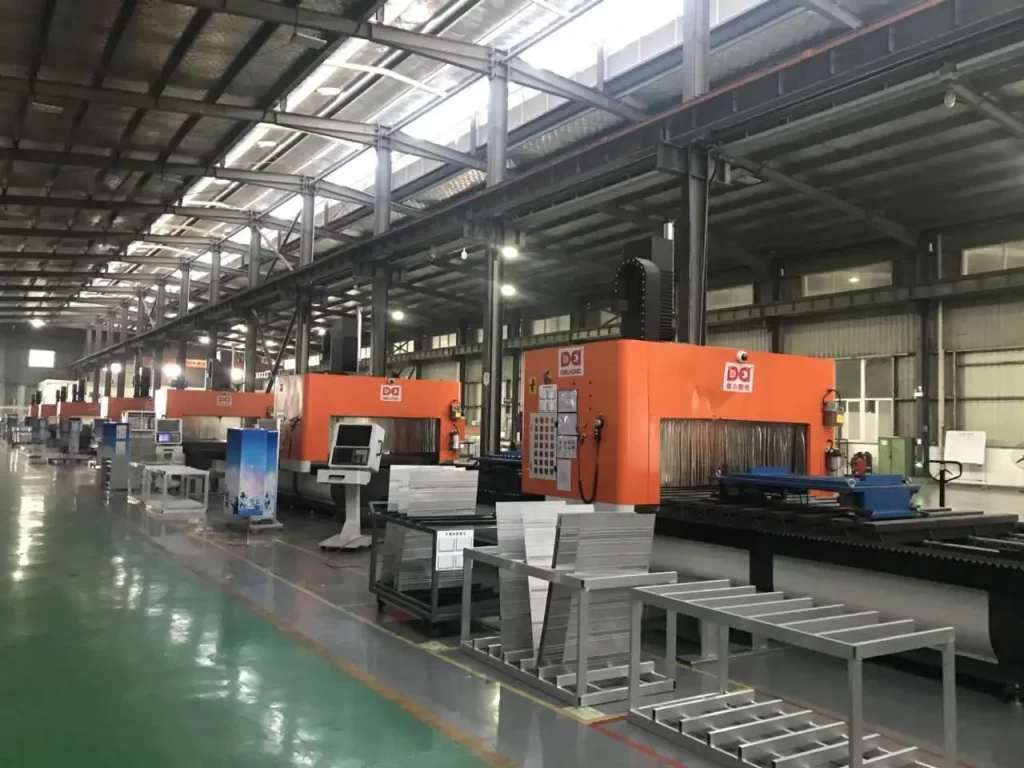

1. How Metal CNC Machines Work
Metal CNC Machines rely on CNC systems and software to guide tools with exceptional precision. Engineers create 3D models in CAD software (like AutoCAD or SolidWorks), defining details such as 0.5 mm bolt holes or 2-meter-long machine beds. These models are converted into G-code (e.g., G01 for linear cuts, G02 for arcs) and M-code (e.g., M03 to start the spindle, M08 for coolant) via CAM software (like Mastercam or NX), instructing the CNC machine to cut, drill, or mill.
For instance, a stainless steel gear’s teeth are machined by a CNC milling machine, keeping tooth thickness tolerances within 0.003 mm. Thread milling with a floating tap holder produces precise internal threads, with real-time monitoring adjusting cutting speeds based on material hardness to avoid errors.
Key Benefits:
- Automation: CNC systems minimize manual intervention. An automotive parts factory boosted batch consistency from 92% to 99.5% using Metal CNC Machines.
- Precision: Tolerances as tight as ±0.005 mm outperform traditional machining (typically ±0.05 mm or more).
- Efficiency: Batch production saves 30% time. For example, machining 100 aluminum brackets takes 5.5 hours with a CNC machine compared to 8 hours manually.
Compared to traditional methods, precision machining boosts efficiency and quality, making it the backbone of precision manufacturing.
2. Applications of CNC Machining

Metal CNC Machines support diverse machining processes, meeting the needs of complex CNC machine parts production. Here are the primary techniques and their applications:
- Milling: Rotating tools cut metal to create flat surfaces, slots, or intricate contours. In aerospace, CNC gantry mills machine aircraft wing ribs in a single setup with ±0.002 mm precision. In automotive, vertical milling machines craft engine block cooling channels.
- Turning: The workpiece rotates while the tool cuts, ideal for cylindrical parts like shafts or bolts. A bearing factory uses CNC lathes to machine inner rings at 3,000 RPM, achieving surface roughness below Ra 0.8 µm.
- Drilling: Precise holes for bolts or medical implants. Medical device manufacturers use CNC machines to drill titanium bone screws with hole diameter errors under 0.01 mm.
- Cutting: Slices metal sheets for electronics enclosures. Smartphone factories use CNC routers to shape aluminum casings at 5 m/min, paired with deburring tools for smooth edges.
- Grinding: Uses grinding wheels for polished surfaces. Mold makers employ CNC grinders to finish mold cavities, achieving surface roughness of Ra 0.02 µm with diamond wheel dressers.
Industry Examples:
- Aerospace: Five-axis CNC machining produces titanium turbine blades, paired with EDM (electrical discharge machining) for blade-hub connections, maintaining ±0.002 mm precision.
- Automotive: CNC lathes machine engine crankshafts with cooling systems, reducing material removal rates by 15%.
- Medical: Titanium joint implants are machined and finished on CNC vertical mills, ensuring biocompatible surfaces.
- Electronics: CNC milling machines create 5G base station heatsinks with 0.3 mm fin thickness and spacing errors below 0.05 mm.
The versatility of these machines makes them essential for demanding machining processes.
3. Core Advantages of Metal CNC Machines
Metal CNC Machines excel in efficiency, precision, and adaptability, offering these benefits:
- Micron-Level Precision: Precision machining achieves ±0.005 mm tolerances, like satellite antenna reflectors with surface errors below 0.01 mm, enabled by CNC systems.
- Consistency: Automated machining processes ensure uniform quality, reducing inspection costs. An appliance manufacturer reported only 3 defective compressor shafts out of 1,000 using CNC machines, compared to 50 with traditional methods.
- Complex Geometries: Five-axis CNC machining handles intricate 3D shapes, like EV battery trays, using automatic tool changers in a single setup.
- High Efficiency: Optimized toolpaths cut cycle times by 20–30% (IndustryWeek, 2024). A gear factory reduced gearbox gear machining time from 12 to 8 minutes with CNC software.
- Material Savings: Precise cuts reduce waste by 15% (DMG Mori, 2023). CNC milling machines limit stainless steel scrap margins to under 5 mm, versus 15 mm for traditional methods.
- Safety: Automation minimizes operator exposure to high-speed tools. Metal CNC Machines with infrared sensors halt operations in 0.1 seconds to protect work areas.
These advantages position CNC machines as the foundation of precision manufacturing.
4. Challenges and Solutions in CNC Machining
Despite their strengths, Metal CNC Machines face challenges. Here are the main issues and solutions:
- High Costs: CNC machines can cost hundreds of thousands to millions, challenging for small businesses. Solution: Modular CNC machines (e.g., “base bed + optional axes”) reduce initial costs by 40%. A mold factory leased equipment, paying 1/30 of the purchase price monthly.
- Technical Complexity: Operating CNC machines requires G-code and CAM expertise, where errors can lead to failures. Solution: CNC programming courses, like DMG Mori’s free “CNC Programming Basics,” cover G-code essentials. User-friendly CNC software auto-generates programs from 3D models.
- Maintenance Costs: CNC repairs and tool replacements increase expenses. Solution: AI-driven CNC software optimizes toolpaths, extending tool life. An aerospace factory extended carbide tool life from 500 to 800 parts by adjusting cutting speeds. IoT diagnostics resolve 70% of common issues, cutting downtime by 6 hours on average.
Emerging Technologies: AI toolpath optimization improves efficiency by 10%, and 5G-enabled CNC machines support real-time diagnostics, boosting equipment uptime from 75% to 88% in an automotive machining shop. These solutions make high-performance machining processes more accessible.
5. Choosing the Right Metal CNC Machines
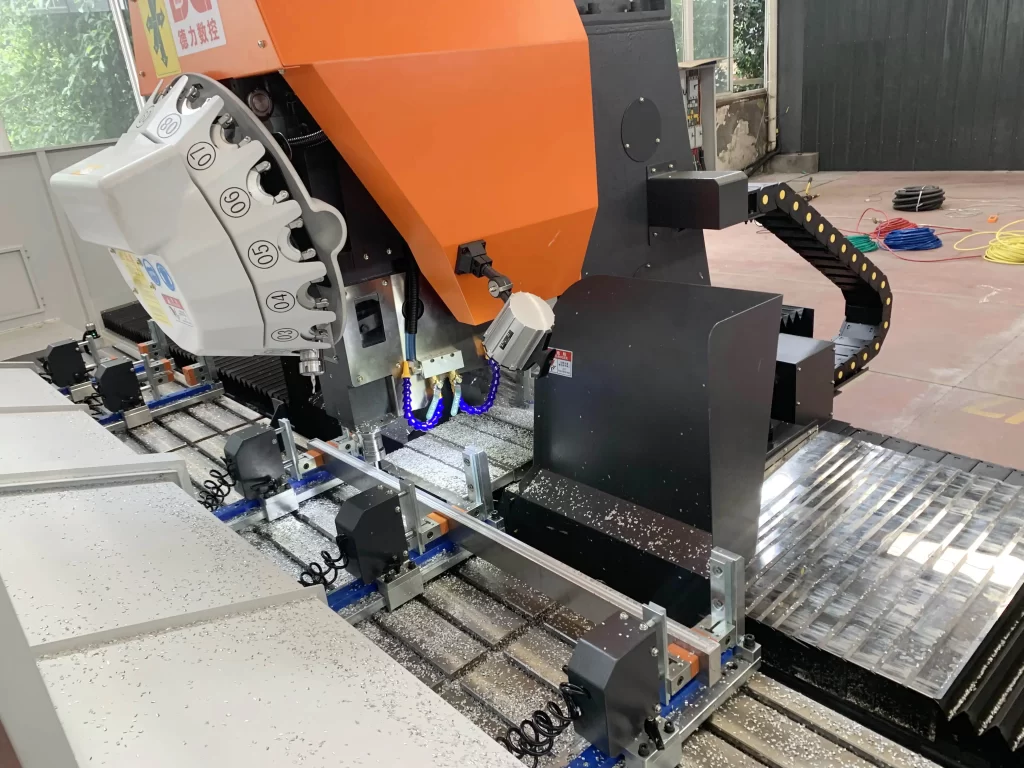

Selecting the ideal Metal CNC Machines requires aligning them with your needs. Key considerations include:
- Material Type:
- Soft metals (aluminum machining, copper): General-purpose CNC routers with spindle speeds above 10,000 RPM, like those for aluminum trim.
- Hard metals (titanium, stainless steel): High-torque CNC milling machines with 2,000–5,000 RPM, such as gantry mills with durable machining tools.
- Part Complexity:
- Simple flat parts: 3-axis CNC milling machines, like horizontal mills for flanges.
- Complex 3D parts: Five-axis CNC machines for multi-angle cuts, like turbine blade milling, with linear guides for stability.
- Key Specifications:
- Spindle Speed: 8,000–15,000 RPM for aluminum, 1,000–5,000 RPM for stainless steel, requiring robust spindle motors.
- Table Size: Must fit part dimensions, e.g., a 1-meter shaft needs a ≥1.2-meter table.
- Control System: Must support CAD/CAM and G-code, with Fanuc or Siemens systems offering strong compatibility.
Matching materials, complexity, and specs ensures efficient production from CNC milling machines for sale. Consult trusted suppliers for CNC machines for sale pricing details.
6. Conclusion
Metal CNC Machines drive precision machining in aerospace, automotive, medical, and electronics, delivering micron-level accuracy and automation. Modular CNC machines, CNC programming courses, and smart CNC software tackle cost and complexity challenges. When selecting Metal CNC Machines, match material hardness, part geometry, and specifications for optimal results. Embrace these machines to achieve efficient, high-quality machining processes in your CNC shop.