CNC machining tools: Types, Uses, Selection Tips
In modern precision manufacturing, CNC machining tools serve as the core execution units of cutting processes. Their performance and compatibility directly determine machining efficiency, surface quality, and process stability. As CNC machine tools evolve toward high speed, high precision, and multi-axis compound processing, the coordinated optimization of CNC cutting tools and tool grinders has become a key factor in enhancing overall manufacturing capability.
From precision regrinding on CNC tool grinders to the efficient integration of CNC machine accessories—such as tool holders, measuring instruments, and automatic tool changers—the entire machining system is advancing toward intelligence and automation. The growing use of 5-axis CNC machine tools and CNC machines equipped with automatic tool changers has driven growing demand for core components like CNC machine automatic tool changers and CNC machine robot loading systems.
This article examines the main types of CNC cutting tools and how they integrate with supporting technologies such as CNC machine measuring tools and CNC machine calibration, to provide manufacturers with a systematic reference on tool selection logic and process matching—while also covering trends in the CNC cutting tools and tool grinders market.
What Are the Basic Requirements for CNC Tools? How to Select Tools Suitable for CNC Machines?
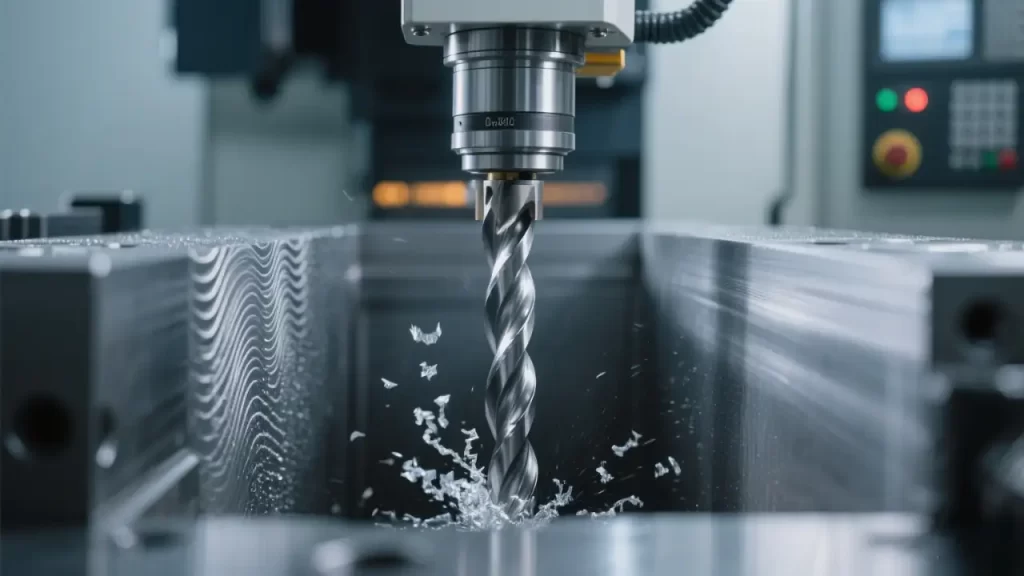

High Rigidity and Anti-Vibration: Avoiding Chatter and Scalloping
In machining centers with spindle speeds as high as 15,000 rpm, tools must resist centrifugal force and cutting impacts. Long overhangs can easily trigger chatter, resulting in surface waviness or scalloping. It is recommended to use variable helix end mills or damped boring bars to suppress resonant frequencies.
Typical Failure Case: A mold shop used a standard-helix Φ10mm flat-end mill to machine deep cavity sidewalls with a 4×D overhang, resulting in obvious vibration marks. After switching to a variable helix tool, surface roughness improved from Ra3.2 to Ra1.6, and tool life increased threefold.
This issue also highlights the importance of broken tool detection systems for CNC machines—real-time monitoring of spindle load or vibration can provide early warnings of tool breakage.
Precise Dimensions and Repeatable Positioning Accuracy
An automatic tool changer (ATC) on a CNC machine requires the overall length and cutting diameter of each CNC machining tool to be controlled within ±0.02mm. It is recommended to use a presetter to measure tools before installation and enter the data into the tool compensation table (D-codes) to prevent overcutting or undercutting due to dimensional deviations.
Currently, technical documentation for CNC machine automatic tool changers (PDF format) is widely used for equipment selection and maintenance reference, covering interface standards such as BT, HSK, and tool change procedures.
Standardized Interface Compatibility: BT, HSK, or SK?
- BT Tool Holder: 7:24 taper, widely compatible, suitable for medium-to-low-speed machining
- HSK Tool Holder: Dual-contact design ensures high concentricity at high speeds, ideal for 5-axis CNC machines
- SK Tool Holder: A European standard commonly found on German-made machines
Ensure full compatibility between the tool holder and the CNC spindle interface to avoid excessive runout that leads to abnormal tool wear. At the same time, the design of CNC machine tool holders and CNC machine tool magazines must also be compatible with the selected tool holder type.
Support for Tool Life Management (TLM) Systems
Modern factories widely adopt TLM systems that automatically issue warnings when a preset cutting time or number of operations is reached. Some high-end CNC tools integrate RFID chips to enable full lifecycle tracking, preventing unplanned downtime.
What Are the Common CNC Milling Tools?

Flat End Mills: The Workhorse for 2D Contour Machining
- Applicable Materials: Carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, engineering plastics
- Typical Applications: Face milling, step surfaces, slotting
- Programming Instructions: G01 linear interpolation + G17 plane selection
- Recommended Strategy: High-feed milling (small depth of cut ap = 0.3–0.5mm, high feed per tooth fz ≥ 1.2 mm/tooth) to improve material removal rate
- Process Limits: Avoid full-edge engagement; recommend arc-in (G02/G03) to reduce impact load
These tools are widely used in CNC milling tool systems, working in conjunction with CNC milling machine automatic tool changers to enable efficient tool changes.
Ball Nose End Mills: The Preferred Choice for 3D Surface Finishing
- Applicable Scenarios: Automotive mold cavities, impeller blades, complex freeform surfaces
- Surface Quality Control: Stepover determines residual height, calculated as: h ≈ 8 × R × f² where f is stepover and R is tool radius. To achieve Ra0.8 or better, stepover should be ≤ 0.2mm
- Multi-Axis Machining: Use A/B-axis linkage to enable continuous 5-axis cutting, avoiding frequent Z-axis lifts
Typical Failure Case: In an impeller machining operation using a Φ6mm ball nose end mill with a 0.5mm stepover, residual height reached 0.015mm, increasing polishing time by 40%. After optimization, stepover was reduced to 0.15mm, achieving target surface finish in a single pass.
Types and Uses of Machining Center Tools

Face Mills: Efficient Large-Area Planar Milling
- Indexable insert design supports rapid replacement, suitable for batch production
- High-feed face milling strategy: Small depth of cut (ap = 0.5–2mm), high feed (fz ≥ 1.5 mm/tooth)
- Through-coolant (internal cooling) interface: Effectively removes chips and prevents built-up edge, especially beneficial when machining aluminum
- Application Example: Rough milling a cast iron platform using a Φ100mm indexable face mill, spindle speed 500 rpm, feed rate 3000 mm/min, reduced single-part machining time by 35%
These tools are a key category of CNC machine cutting tools, widely used in the CNC metal cutting machine market.
Mini Face Mills for Live Tooling (Turn-Mill Applications)
- Used in CNC lathe tool systems to perform face milling
- Tool Selection: Short cutting edge, high rigidity (Φ20–Φ50)
- Typical Applications: Flat surfaces, square slots, cross slots on shaft parts
Note: Keep overhang length ≤ 3×D to prevent vibration from affecting surface quality.
What Types of CNC Drills Are Available? How to Choose?
Center Drills: Locating Before Drilling
- Type A: Taper + straight hole only, used for drill guidance
- Type B: Includes a protective chamfer to preserve the 120° taper, suitable for subsequent centering with a tailstock center
- Programming Standard: Perform a center drilling operation once before G81/G82 drilling cycles
- Failure Cause: Drilling without centering can cause twist drills to deviate, resulting in hole position errors exceeding 0.1mm
Twist Drills (Internal Coolant Type): The Mainstay for Deep Hole Machining
- Internal coolant channels deliver high-pressure coolant to flush out chips and prevent clogging
- Deep hole chip removal strategy: Use peck drilling cycles (G73/G83), retracting every 5–10mm to clear chips
- Tool Monitoring: Monitor spindle load to detect drill wear or blockage
Step Drills: One-Pass Multi-Diameter Holes
- Advantage: Eliminates tool changes, reducing program blocks and cycle time
- Applicable Scenarios: Mounting plates for electrical enclosures, flange hole patterns, thin sheet parts
- Limitations: Only suitable for soft materials (aluminum, low-carbon steel) and shallow holes (depth < 3× diameter)
How High-Precision Can CNC Boring Tools Achieve?
Fine Boring Tools: Tolerances Within ±0.005mm
- Micrometer adjustment mechanism with 0.01mm graduation accuracy, suitable for IT6–IT7 grade holes
- Integrated with Renishaw probes: Automatic measurement → feedback compensation → closed-loop control
- Applicable Parts: Engine blocks, bearing housings, hydraulic valve bodies
Such high-precision machining relies heavily on CNC machine measuring tools and CNC machine calibration systems.
What Tools Are Used for CNC Threading? Taps or Thread Mills?
Thread Mills: A More Flexible Option
- One tool can machine multiple thread diameters via coordinate offset
- Supports non-circular threaded holes (e.g., oval holes)
- No blind-hole chip evacuation issues, ideal for difficult-to-machine materials like stainless steel and titanium alloys
- Programming Command: G03 helical interpolation
- Recommended Scenarios: M12 and larger threads, batch production, high-hardness materials
Compared to traditional taps, thread mills are better suited for complex programs written by CNC machine programmers, reducing the frequency of CNC machine tool changes.
What Are Specialized CNC Tools?
T-Slot Cutters: Milling Worktable Slots
- Multi-stage program control for layered cutting to avoid overload
- Tool Structure: Equipped with a guide post to prevent deviation
Keyseat Cutters: Direct Plunge Cutting for Blind Keyways
- Two-flute end-cutting design provides axial cutting capability
- No pre-drilling required, simplifying the process
Chamfering Tools: Automated Deburring
- Integrated at the end of the main program to automatically chamfer all hole edges
- Indexable insert design reduces downtime
These tools fall under the category of CNC machine deburring tools, improving automation in post-processing.
What Materials and Coatings Are Used for CNC Tools?
Base Material Comparison
| MATERIAL | APPLICABLE SCENARIOS | FEATURES |
|---|---|---|
| Carbide | Mainstream choice | High hardness, suitable for high-speed spindles |
| High-Speed Steel (HSS) | Low-speed, small-batch | Low cost, good toughness |
| Cermet | Aluminum finishing | High surface finish |
| CBN | Dry cutting of hardened steel | Heat-resistant, long life |
Common Coatings and Their Functions
| COATING | COLOR | APPLICABLE MATERIALS | ADVANTAGES |
|---|---|---|---|
| TiN | Gold | General steel | Improves wear resistance |
| TiAlN | Purple-black | Stainless steel | Heat-resistant, oxidation-resistant |
| AlTiN | Dark gray | High-speed dry cutting | Oxidation temperature up to 900°C |
| DLC | Glossy black | Aluminum | Prevents adhesion, reduces built-up edge |
Tip: Use thin coatings (1–2μm) for finishing, thick coatings (4–6μm) for roughing.
Tool Resharpening and CNC Tool Grinders
CNC tool grinders are core equipment for ensuring tool life and precision. CNC tool grinder prices vary by brand, accuracy, and level of automation, with mainstream models ranging from RMB 200,000 to 1,000,000.
5-axis CNC tool grinders can perform high-precision resharpening of complex tools (e.g., ball nose end mills, helical cutters), widely used in production systems of CNC tool grinder manufacturers.
Selecting the best combination of CNC cutting tools and tool grinders requires comprehensive consideration of workpiece material, tool type, production capacity, and maintenance costs.
How to Select CNC Machining Tools Using CAM Software?
Build a Realistic Tool Library
Define the following in Mastercam, Hypermill, Siemens NX:
- Geometric parameters (D, L, number of flutes)
- Recommended cutting parameters (Vc, fz, ae, ap)
- Tool holder models (for collision detection)
Path Simulation and Interference Checking
Use virtual environments to detect interference between long-overhang tools and fixtures, allowing early optimization of workholding setups and avoiding collisions during actual machining.
This process also depends on the rationality of CNC machine design and the precise installation of tool magazines and tool holders by CNC machine assemblers.
Tool Combination Strategies for Different Machining Scenarios
Mold Machining Tool Setup
| OPERATION | RECOMMENDED TOOL | PROCESS NOTES |
|---|---|---|
| Rough Milling | Φ12mm corner-radius end mill | High-feed milling to remove large allowances |
| Semi-Finishing | Φ6mm ball nose end mill | Stepover ≤ 0.2 mm, continuous 5-axis machining |
| Corner Cleaning | Φ2mm small-diameter ball nose end mill | Manual programming or dedicated clearing paths |
| Hole Machining | Fine boring bar + thread mill | Avoid tap breakage, improve consistency |
Aerospace Aluminum Structural Parts
| OPERATION | RECOMMENDED TOOL | PROCESS NOTES |
|---|---|---|
| High-Speed Milling | Large-helix-angle end mill (rake angle ≥40°) | Spindle speed ≥12,000 rpm, anti-built-up edge |
| Deep Hole Drilling | Internal coolant twist drill + G83 peck drilling | Segmental chip removal to prevent drill breakage |
| Deburring | Chamfering tool integrated at program end | Enable automated post-processing, replace manual work |
Batch Production of Stainless Steel Flanges
| OPERATION | RECOMMENDED TOOL | PROCESS NOTES |
|---|---|---|
| Facing | Indexable face mill | Fast insert replacement, suitable for continuous operation |
| Hole Pattern | Step drill, one-pass forming | Reduce tool changes, improve cycle time |
| Threading | Thread mill instead of tap | Prevent breakage, suitable for M16+ large threads in batch production |
Conclusion
In the pursuit of “quality improvement and efficiency enhancement,” CNC machining tools have evolved into the nervous endings of the entire manufacturing system. From the precise matching of CNC cutting tools and tool grinders to the efficient coordination of CNC machine automatic tool changers and CNC machine robot loading systems, the entire system is moving toward intelligence.
Continuous innovation in 5-axis CNC machines, CNC milling machine tool changers, and CNC machine tool holder types is driving growth in the CNC metal cutting machine market. Meanwhile, trends in CNC tool grinder manufacturers and CNC tool grinder pricing reflect strong industry demand for high-precision resharpening equipment.
Only by placing “tool selection” within the broader manufacturing chain—integrating material properties, machining stages, equipment capabilities, and typical failure modes—can we truly transition from “being able to machine” to “efficient, stable, and intelligent machining.”