CNC Machines vs. 3D Printers: Are They the Same?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines and 3D printers represent two pillars of modern manufacturing, yet they operate on fundamentally different principles. CNC machines use subtractive manufacturing—removing material to achieve precise shapes—while 3D printers rely on additive manufacturing, building objects layer by layer. This article explores their definitions, technologies, applications, and how they complement each other in today’s manufacturing landscape.
1. Overview of CNC Machines
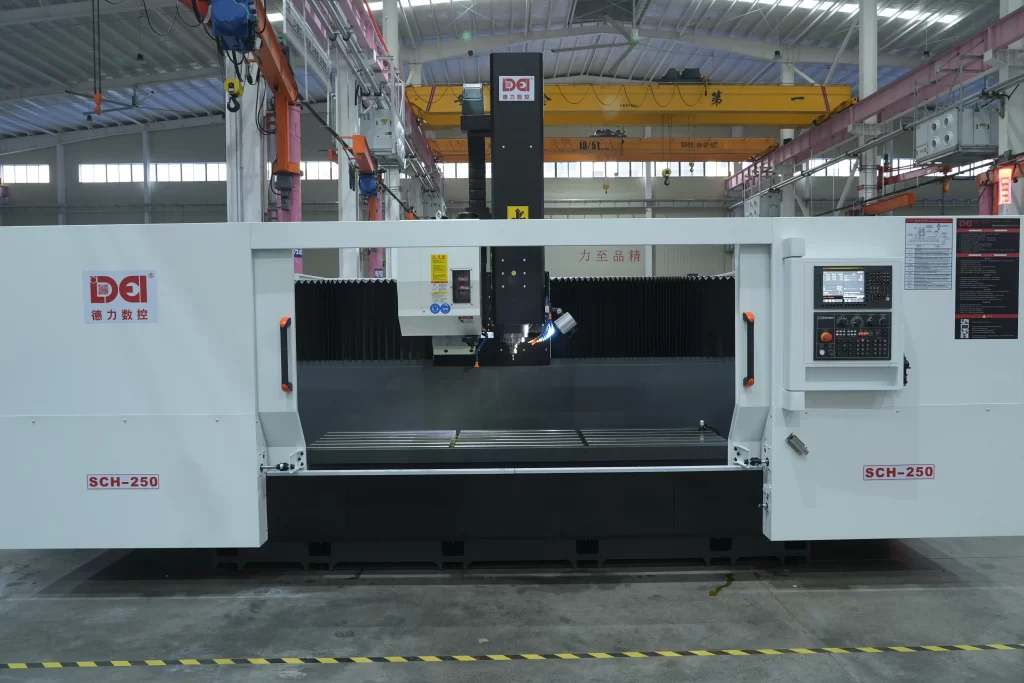

Definition and Working Principle
CNC machines are foundational tools in industrial production. Engineers use CAD software to design parts and CAM software to generate G-code, which guides the machine’s operations. Material is secured on a worktable, and cutting tools remove unwanted sections to form high-precision parts. Subtractive manufacturing is especially suited for high-strength materials and precision engineering.
Types of CNC Machines
– CNC Milling Machines: Rotating tools carve 3D shapes, ideal for mold making.
– CNC Lathes: Workpieces rotate against a fixed tool, perfect for cylindrical parts like bolts.
– CNC Cutting Machines: Includes laser cutters for fine details and plasma cutters for thick materials.
Applications
– Automotive: Engine parts, frames.
– Aerospace: Turbine blades, structural components.
– Woodworking & Metalworking: Furniture carving, custom parts.
– Small Workshops: Art, design, and bespoke products.
2. Overview of 3D Printers
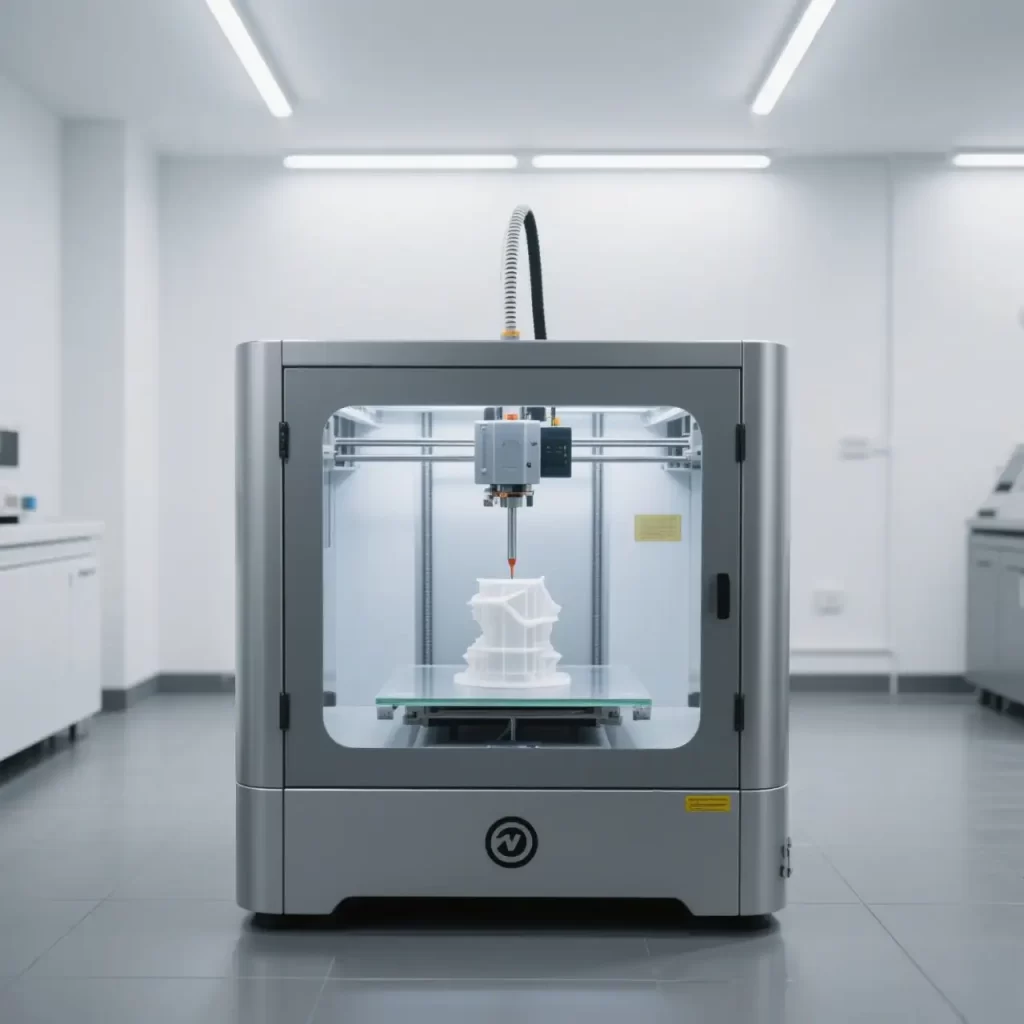

Definition and Working Principle
3D printers work through additive manufacturing. CAD designs are sliced into layers, and the printer builds the object from materials such as plastics, resins, or metal powders. They excel in producing complex, intricate designs.
Main Technologies
– FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling): Melts plastic filament for low-cost prototyping.
– SLA (Stereolithography): Cures liquid resin with a laser, offering fine detail.
– SLS (Selective Laser Sintering): Sintering powdered material for industrial-grade strength.
Applications
– Rapid Prototyping: Fast design validation.
– Medical: Customized prosthetics, dental molds.
– Art and Consumer Goods: Personalized phone cases, jewelry, sculptures.
3. CNC vs. 3D Printing: A Comparison
| Aspect | CNC Machines | 3D Printers |
| Manufacturing Method | Subtractive (cutting/removal) | Additive (layer-by-layer building) |
| Materials | Metals, wood, plastics | Plastics, resins, metal powders |
| Precision | Micron-level precision, high durability | Good for complex shapes, moderate finish |
| Cost & Efficiency | High setup cost, fast for large batches | Low entry cost, slower, best for small runs |
| Limitations | Material waste, complex shapes hard | Material strength varies, slower process |
Summary:
– CNC: Ideal for durable, precision parts in metal or wood.
– 3D Printing: Ideal for rapid prototyping, custom complex designs.
4. Hybrid Manufacturing & Trends
Complementary Use
CNC and 3D printing can be combined in hybrid workflows. For example, 3D printers can create complex forms, followed by CNC machines for precise finishing. This is widely used in aerospace and medical fields.
Technological Advancements
– CNC: AI-optimized tool paths, automation.
– 3D Printing: New materials (composites, biodegradable resins).
– Hybrid Equipment: Emerging systems with both additive and subtractive functions.
5. Choosing the Right Tool
Choose CNC if:
– You need micron precision or industrial strength.
– You’re working with metals or wood.
– You require high-speed large-batch production.
Choose 3D Printing if:
– You need design iteration and prototyping.
– You require hollow or intricate internal geometry.
– You work with low-volume or customized designs.
6. Conclusion
CNC machines provide strength and precision through subtractive manufacturing, making them indispensable in traditional industry. 3D printers offer flexibility and creativity via additive methods. These technologies are not rivals—they are complementary. Together, they empower the future of smart, efficient, and innovative manufacturing.
Want to learn more or explore which solution fits your production needs? Let’s connect and discuss!printers? Feel free to leave a message in the background, and let’s explore together!